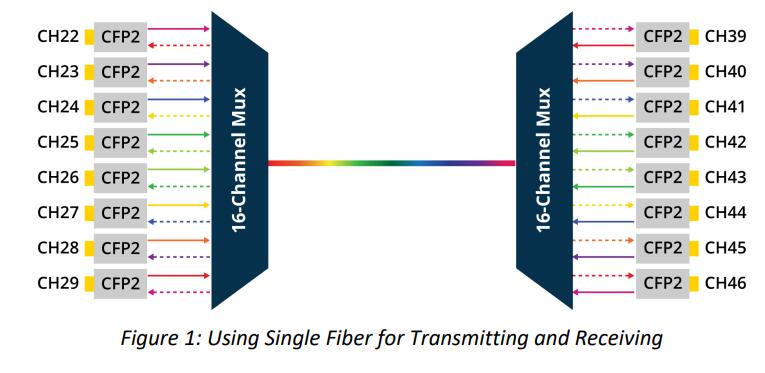
Fiber optic networking used to require two fibers, one for transmitting and one forreceiving signals simultaneously. Single fiber solutions emerged as a way to reduce costs ofdark fiber solutions and optimize fiber. Rather than using two dedicated strands, a single fiber strand that carries a bi-directional signal is used.
For enterprises leasing dark fiber from providers, the operational savings are significant. The challenge is to maximize revenues while reducing their largest expenditure - monthly cost of the fiber link. Using single fiber reduces operational costs by 50%, making dark fiber an affordable solution.
In DWDM, active and passive solutions for single fiber transmission range from 4 up to 8 400G wavelengths, with optional optical amplifiers. The single fiber solution seamlessly
integrates with any standards-based 10/25/100Gb Ethernet, 16/32G Fibre Channel, and OTU2/2e/4 client interfaces, and supports any mix of up to 400G services.
Single fiber solutions are recommended for the following applications:
• Point-to-point, ring or linear add and drop topologies, where installing new fiber is difficult or expensive
• Enables splitting enterprise traffic over two different fibers as opposed to using the same fiber for the entire traffic
• Increase reliability to an existing dual fiber solution by using one fiber for transmitting and receiving, and one for protecting.
The single fiber solution is more efficient and economical for many applications and needs, and provides the same performance and throughput as the traditional dual fiber solution. It enables customers to utilize single fiber for both transmitting and receiving, significantly maximizing their investment and reducing costs such as monthly leasing, taxes, or laying additional fibers.
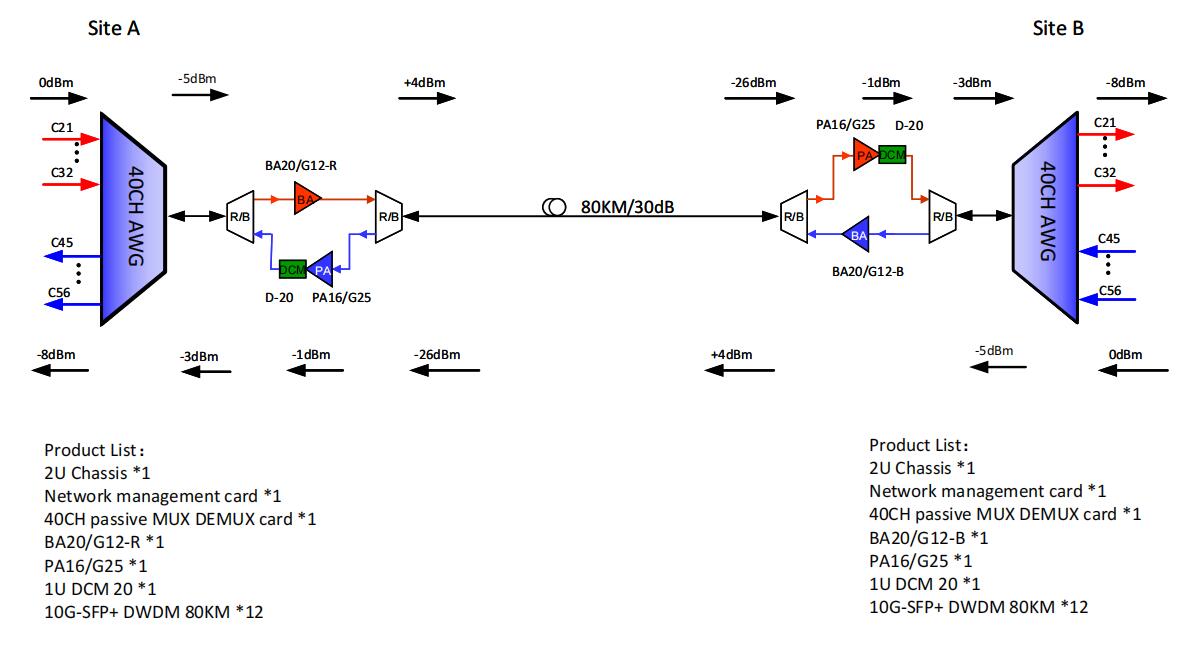
The solution is transparent to the client optical interface and suits 400G, 100G, 10G, and sub-10G with any client interface mix. It incorporates a single mux with 8 or 16 channels. Half of the mux is used for transmitting and half for receiving.
If you need single fiber soluiton, welcome to contact HTF team, HTF will help you design the suitable DWDM solution. Support single fiber or dual fiber.
www.htfuture.com ivy@htfuture.com +8618123672396